Muscle: The Three Types of Muscle
Contractility is a fundamental property of cells and the majority of
them contain essentially the same contractile machinery as that found
in muscle cells. In muscle cells, however, a larger proportion of the
cells' resources are given over to this function than in other cell types.
These are the three types of muscle:
Skeletal Muscle
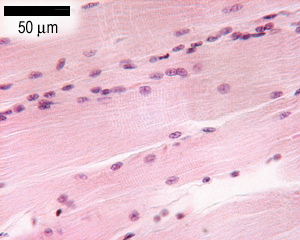
Contractions move part of the skeleton. Also called 'voluntary'
because usually its contractions are under your control.
It has a stripy appearance, because of the repeating structure
of the muscle: there are many myofibrils (fibers), each one of which
is made up of repeating units called muscle sarcomeres. Each sarcomere is 2.5 mm long. Can you
work out how many sarcomeres are there (placed end to end) in your
biceps muscle, which approximately 25cm long?
(click here to find out more)
Cardiac Muscle
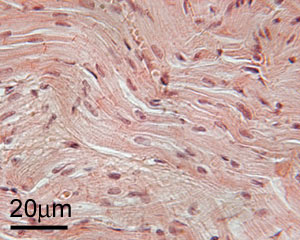
Cardiac muscle makes up the muscular walls of the heart (myocardium).
It is 'involuntary' because its contractions are not under your
control. However, it has a similar ultrastructural organisation
to skeletal muscle. So, it too has a stripy appearance because of
the repeating units called muscle sarcomeres.
(click here to find out more)
Smooth Muscle
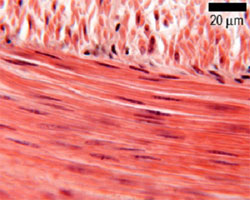
Found in the walls of most blood vessels and tubular organs such
as the intestine. It is also 'involuntary'. However, it does NOT
have a stripy appearance, because it does not have repeating sarcomeres.
The contractile proteins, myosin and actin are much more randomly
arranged than in skeletal or cardiac muscle
(click here to find out more)
Skeletal Muscle and Cardiac Muscle are also called 'striated muscle',
because they have dark and light bands running across the muscle width
when they are looked at under the microscope.
Confusingly the prefixes myo- and sarco- (respectively
from the Latin and Greek, both meaning muscle) are often used when naming
structures and organelles associated with muscle.
Thus the plasma membrane of muscle cells is sometimes called the sarcolemma
and their cytoplasm sarcoplasm.
Their endoplasmic reticulum is called sarcoplasmic reticulum and
their mitochondria are sometimes called sarcosomes.
The contractile fibres that lie in the sarcoplasm are known as myofibrils
and the embryonic precursors of skeletal muscle cells are called myoblasts.


