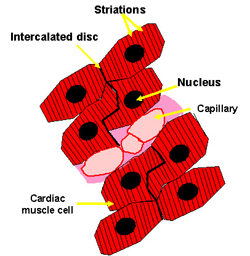
Cardiac muscle is striated, like skeletal muscle, as the actin and myosin are arranged in sarcomeres, just as in skeletal muscle.
However, cardiac muscle is involuntary.
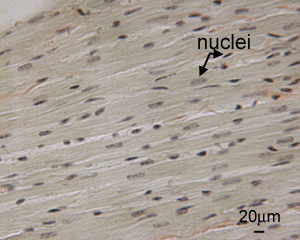
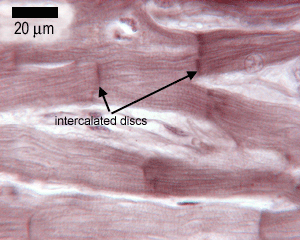
Cardiac muscle cells usually have a single (central) nucleus. The cells are often branched, and are tightly connected by specialised junctions. The region where the ends of the cells are connected to another cell is called an intercalated disc.
The intercalated disc contains gap junctions, adhering junctions and desmosomes.
Gap junctions allow the muscle cells to be electrically coupled, so that they beat in synchrony.